DNS Lookup
Created on 17 October, 2025 • Checker tools • 85 views • 2 minutes read
A DNS lookup is a foundational process in internet networking that converts human-friendly domain names (like www.example.com)
DNS Lookup: How Domain Name System Resolves Website Addresses
Understanding DNS Lookup
A DNS lookup is a foundational process in internet networking that converts human-friendly domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses. This vital step allows your browser or device to locate and connect to websites, applications, and online resources seamlessly. Every time you type a URL or click a link, a DNS (Domain Name System) lookup happens behind the scenes, streamlining your online experience.
What is DNS?
DNS stands for Domain Name System—a decentralized directory of domain records. Think of it as the “phonebook of the internet.” Instead of remembering complex numerical IP addresses, users rely on DNS to quickly translate website names into addresses computers can understand.
Why DNS Lookup Matters
Without DNS lookups, users would struggle to navigate the web, entering long strings of digits rather than memorable URLs. DNS makes websites more accessible, improves load speed, and is essential for email routing, file sharing, and cloud services.
How DNS Lookup Works
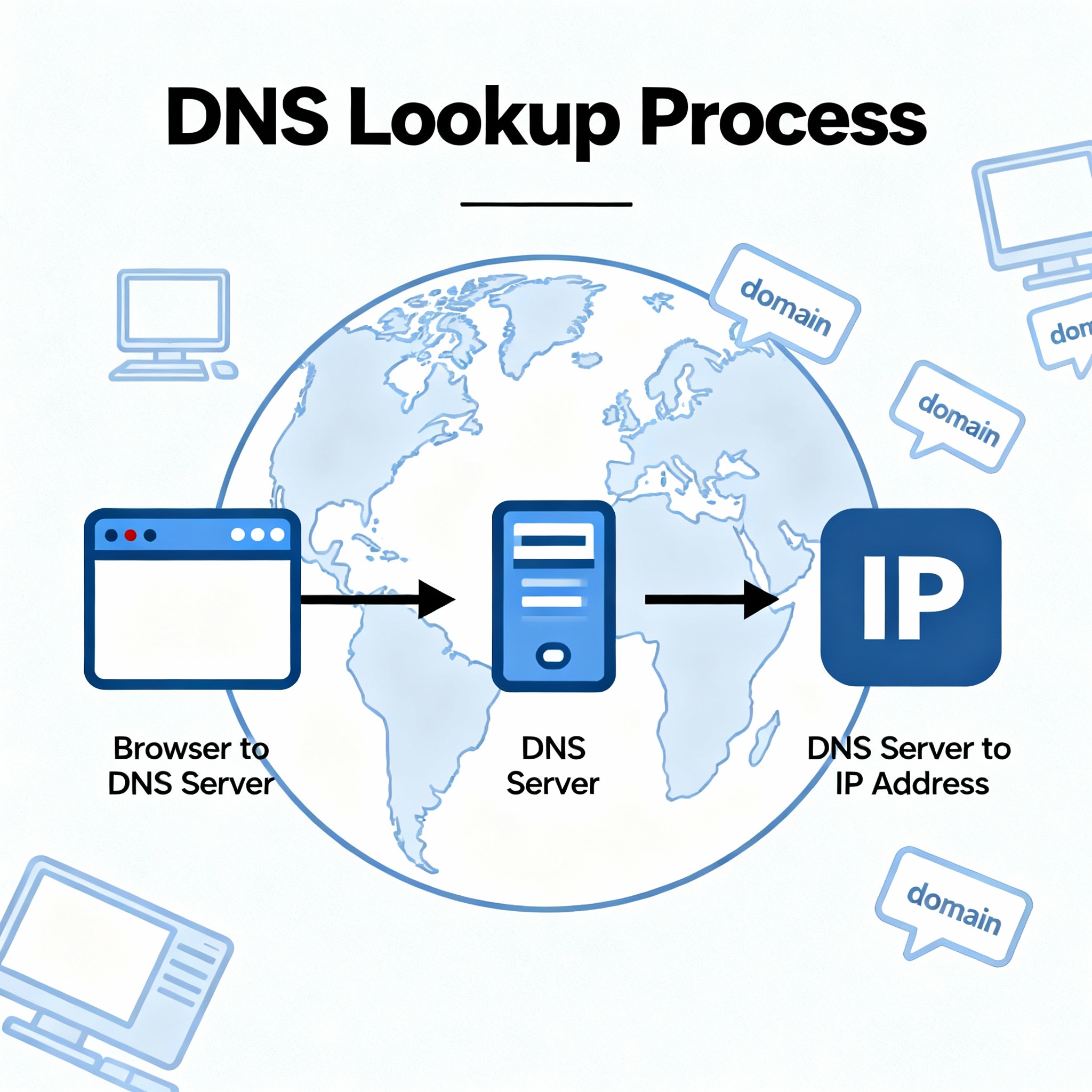
Step-by-Step Process
- User Request: You enter a domain name in your web browser.
- DNS Resolver: Your query goes to a DNS resolver, usually provided by your ISP.
- Recursive Search: The resolver checks its cache or asks other DNS servers for the answer, starting with the root server, then the TLD (“top-level domain”) server, and finally the authoritative server for the requested site.
- Return IP Address: Once the resolver finds the correct IP address, it passes the information back to your browser, which connects to the server, loading the website.
Types of DNS Lookup
- Forward DNS Lookup: The most common type, converting a domain name to an IP address.
- Reverse DNS Lookup: Finds the domain name associated with a given IP address, useful for security and email validation.
Advanced DNS Lookup Features
DNS Caching
To speed up repeated visits and conserve network resources, DNS resolvers store recently looked-up addresses in cache. This reduces lookup times and bandwidth but can sometimes lead to accessing outdated records if sites change server addresses.
DNS Propagation
When you update DNS settings for a domain, it takes time—typically 24 to 48 hours—for changes to spread (“propagate”) across global DNS servers.
DNS Security Concerns
DNS is vital for web security. Attackers may exploit DNS to redirect users, hijack traffic, or launch denial-of-service attacks. Modern DNS protocols—like DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions)—help protect against these threats by authenticating server responses.
Conclusion
DNS lookup is the backbone of internet communication, making websites accessible and connecting users to online resources. Understanding how DNS lookup works, its types, and its security relevance helps individuals and businesses manage domains efficiently and stay safe online.
Popular posts
-
GIF to BMPImage Manipulation tools • 583 views
-
GIF to WEBPImage Manipulation tools • 462 views
-
GIF-to-PNGImage Manipulation tools • 363 views
-
SHA-3/512 generatorConverter tools • 292 views
-
GIF to JPGImage Manipulation tools • 257 views